Date: 26th July 2017
Time: 8.15 am- 10.05 am
Venue: Al Bukhari Library
Conducted by: Madam Nur Fitriah
Assalamualaikum and hi, Alhamdulillah we meet again! So, for this week's topic, it's about on of the famous location in UiTM Jengka, and it is library! And it's name is Al- Bukhari Library. So, in this post, I am going to write about library and campus resources. So, as usual, let's get started!
Background of Al- Bukhari Library
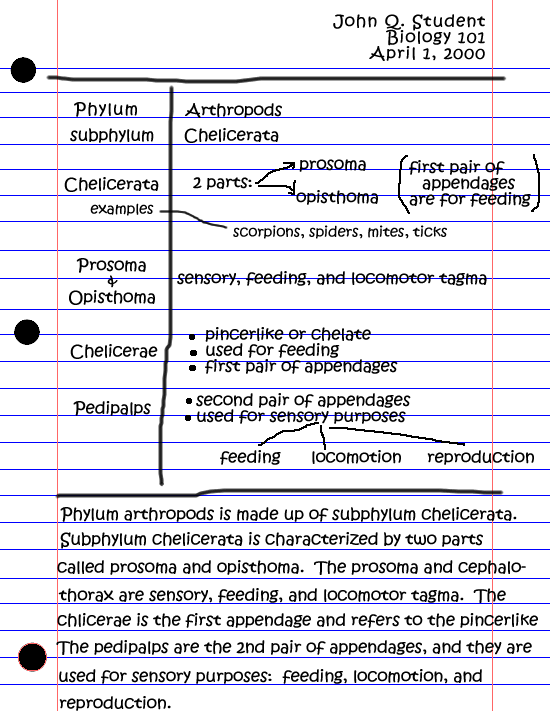
Al- Bukhari Library was first built in January 1985, located at Teluk Sisek, Kuantan. In June 1993, this library has moved to Bandar Jengka and known as Al- Bukhari Library.
In July 2011, Al- Bukhari Library have received brand new building and it starts operating on 2nd April 2012. This new library can fit 1511 seats. The books in this library classified based on Library of Congress (LCC) system.
Types of Resources
There are 3 types of campus resources that you need to know;
|
|
Example
|
|
|
|
Library, Information Technology & Computer, Registrar
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Al-Bukhari Library capacity
Reading space: 818 seats
Discussion room: 2 rooms (8 seats per room)
IT room: 80 seats
Training room: 36 seats
Total seats: 1030 seats
10 thing you MUST KNOW about Al- Bukhari Library
1. Operation hours of Al Bukhari 1 & 2 Library
|
Operation hours of Al- Bukhari 1 & 2 Library table
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Borrowing & Returning Books
We can renew the date of the borrowed books. For diploma and degree students, they can borrow 20 books at a time.
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
PRA DIPLOMA
|
|
|
|
|
||||
3. Steps to borrow and return books
a. Search the book you wanted using OPAC (Online Public Access Catalog)
b. When you find the book you wanted to borrow using OPAC, search the book at the shelves according to OPAC. Shelves A- P at the 1st floor while shelves Q- Z located at the 2nd floor,
c. Make sure to bring your matric card with you to identify yourself.
d. Go to borrowing counter or you can go to KIOSK Self- Check Machine
4. Fine
Students will be fined RM 0.20 for each day and each book if they do not return the book the day they were supposed to. They are not allowed to borrow other books if they do not pay the fine.
5. Missing books
Steps to do if you lost the library books
a. Make sure you search it carefully
b. Make a report to library to avoid paying more fines
c. Students will be given 14 days to find the exact books they lost
6. The borrowing process between other libraries
If the students can't find the books they wanted to borrow at Al- Bukhari library, the students can request at the counter to borrow the books at other library. The books will be borrowed from other library.
7. IT Room Usage
- Students have to register their names at the counter of the IT room
- Students are not allowed to save personal data in the computer of IT room
- Students have to renew their registration every 1 hour they use the computer for usage statistic
- Students are not allowed to bring any software into the IT room
- Students are not allowed to steal the computer tools and devices
8. Library Zone
There are 3 zones in the library;
Silent Zone
Any conversation in this room is not allowed. The environment in this zone must be quiet. Mobile phone usage is not allowed.
Quiet Zone
Students must lowered their voice. Conversations are allowed but wih a low voice. The mobile phones must be set in silent mode.
Social zone
Discussions can be comfortably done in this zone but with controlled volume of their voices.
9. i- Book KKM
This feature is a website to find End Notes Software, Online Databases and Research Work Modules. To access this site, you must visit Al- Bukhari Library website. Then, click i-Book KKM on the right column and click Place Reservation and choose a module. Fill in the information.
10. URL
Al- Bukhari Library staffs can be contacted through these URL;
a. https://www.facebook.com/puitmpahang
b. http://library.pahang.uitm.edu.my/v1/index.php
c. http://libphg.blogspot.my/
How to READ BOOK?
- Table of Content
- Index
- Back of the book/ summary
Whats is APA style?
APA (American Phsychological Association) style is most commonly used to cite sources within social sciences.
How to do citation in APA style?
I think that's all from me for this post today. I hope it can help you to know more about our library and campus resources! ✌ Till we meet again, Insyaallah. Goodbye! ☺❤